Graphite Gland Packing: The Versatile Sealing Solution
 2025.06.26
2025.06.26
 Industry News
Industry News
Graphite gland packing is a cornerstone in industrial sealing, prized for its exceptional performance in demanding environments. This article delves into the fundamental characteristics of graphite gland packing, its various types, installation best practices, and how it stacks up against other common sealing materials.
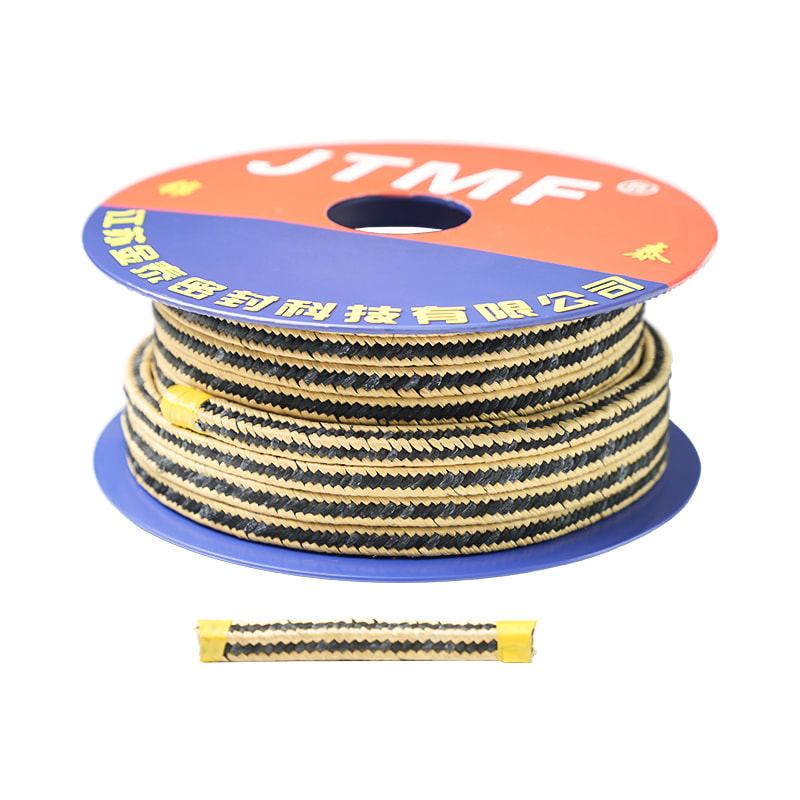
Cord Graphite Aramid Fiber Zebra Braided Gland Packing With Oil
Fundamental Characteristics of Graphite Gland Packing
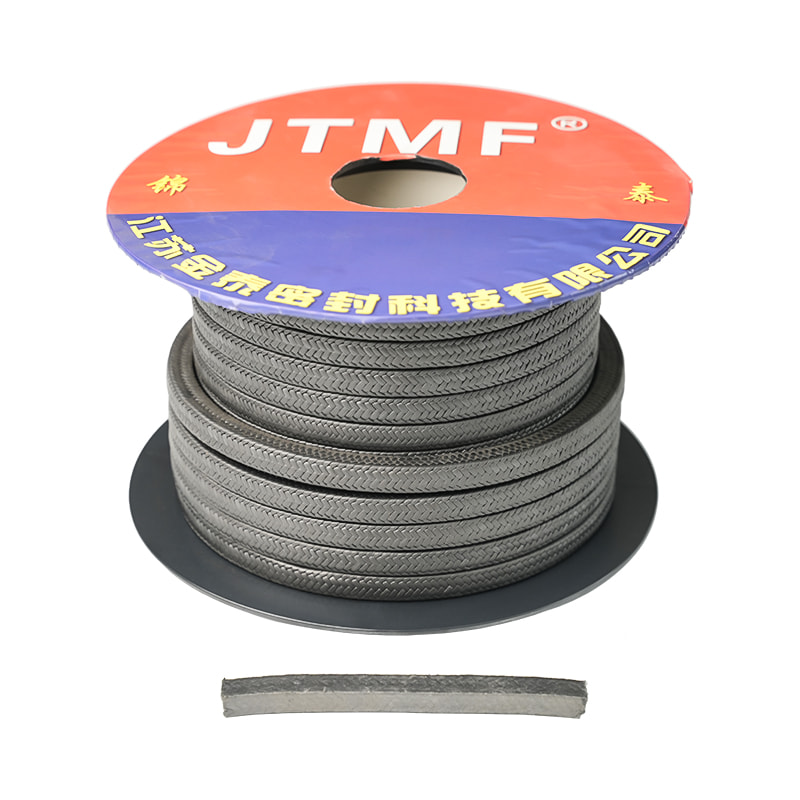
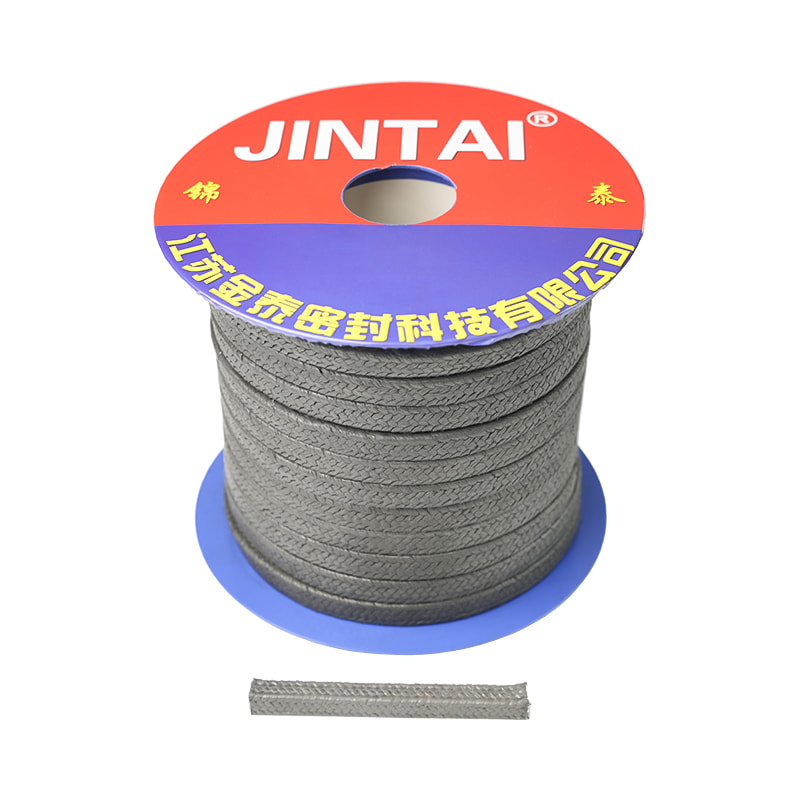
Graphite gland packing is a high-performance sealing material primarily composed of flexible graphite. This material's unique lamellar structure allows it to be compressed and expanded, creating a tight and resilient seal. It can be found in various forms, including braided graphite, where flexible graphite ribbons or yarns are woven into a dense packing.
The key to graphite packing's widespread use lies in its remarkable properties:
- High Temperature Resistance: Graphite gland packing can withstand extreme temperatures, often exceeding 800°C (1472°F) in non-oxidizing environments, making it ideal for high-temperature applications like steam lines and exhaust systems.
- Corrosion Resistance: It exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of corrosive media, including acids, alkalis, and solvents, ensuring longevity in harsh chemical processing environments.
- Self-Lubricating Properties: The inherent lubricity of graphite reduces friction between the packing and the moving shaft or stem, minimizing wear and tear on both components.
- Low Friction Coefficient: This property contributes to reduced power consumption and cooler operation, enhancing the efficiency of equipment like pumps and valves.
These characteristics make graphite gland packing suitable for a diverse range of applications, including pumps, valves, mixers, and reaction vessels, especially in environments characterized by high temperatures, high pressures, or corrosive media.
Types of Graphite Gland Packing and Selection Guide
Graphite gland packing comes in several forms, each designed to meet specific operational requirements.
Common Types:
- Pure Graphite Gland Packing: This type consists solely of flexible graphite, offering maximum temperature and chemical resistance. It's often used in critical applications where purity is paramount.
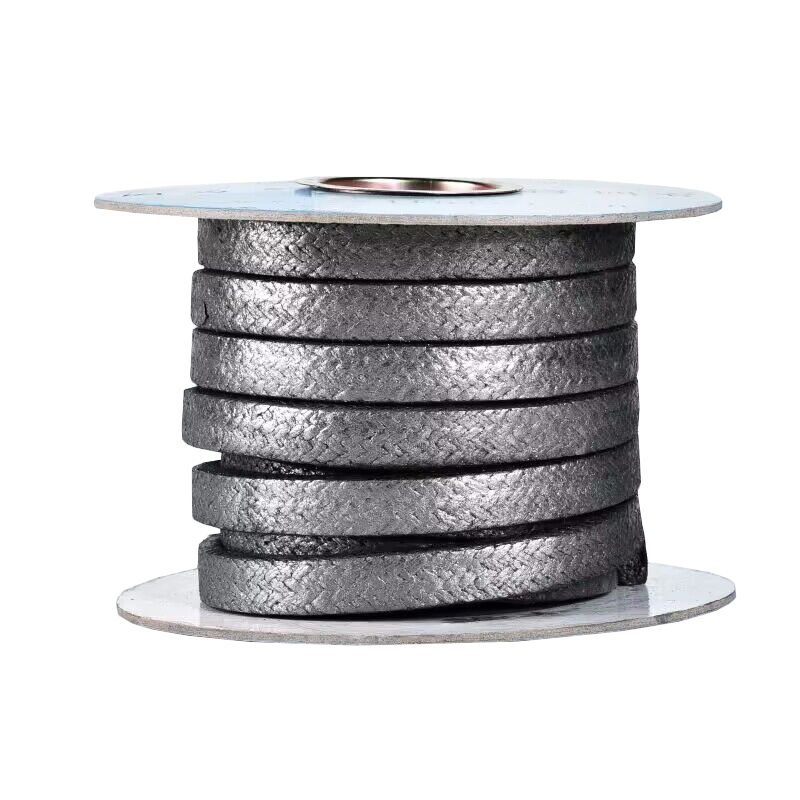
- Metal-Reinforced Graphite Gland Packing: To enhance mechanical strength and extrusion resistance, graphite packing can be reinforced with metallic materials like Inconel wire. This type is particularly well-suited for high-pressure applications and dynamic sealing.
- Hybrid Fiber Graphite Gland Packing: Some packing incorporates other fibers, such as carbon fiber, alongside graphite. This combination can offer improved wear resistance or enhanced sealing capabilities in specific conditions.
Selection Factors:
Choosing the correct graphite gland packing is crucial for optimal performance. Consider the following factors:
- Medium Type: The chemical compatibility of the packing with the process fluid (e.g., acids, alkalis, steam, hydrocarbons) is paramount to prevent degradation and ensure a long service life.
- Temperature/Pressure Range: The operating temperature and pressure of the application dictate the required heat and pressure resistance of the packing material.
- Shaft/Stem Movement Speed: For dynamic applications involving rotating shafts or reciprocating stems, the packing's ability to withstand friction and wear at specific speeds must be considered.
Installation and Replacement Steps for Graphite Gland Packing
Proper installation is key to the effectiveness and longevity of graphite gland packing.
Installation Preparation:
Before installing new packing, thoroughly clean the stuffing box or sealing chamber, removing any old packing material, debris, or corrosion. Measure the dimensions of the stuffing box (shaft diameter, stuffing box bore, and depth) to ensure you cut the packing rings to the correct size.
Layered Filling Technique:
Cut the packing into individual rings, ensuring clean, precise cuts. Install the rings one by one, using an alternating or staggered cut technique (like a spiral or butt joint) to prevent leakage paths. Each ring should be firmly seated before the next is added. Avoid over-compressing the packing during installation, as this can lead to excessive friction and heat buildup.
Common Mistakes:
- Over-tightening: Applying too much compression can cause the packing to overheat, accelerate wear, and potentially damage the shaft or stem.
- Irregular Cuts: Poorly cut packing rings create gaps and uneven surfaces, compromising the seal's integrity and leading to premature leakage.
Common Problems and Solutions
Even with proper installation, issues can arise.
Leakage Causes:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, packing material naturally wears down due to friction, leading to leakage.
- Media Corrosion: Incompatible media can degrade the packing, reducing its sealing effectiveness.
- Improper Installation: As mentioned, incorrect cutting, inadequate compression, or misalignment can result in leaks.
Maintenance Suggestions:
Regular inspection of the gland area for signs of leakage or wear is essential. In some applications, particularly with older or less lubricious packing types, periodic lubrication replenishment (if applicable to the specific packing design) can extend service life and reduce friction. Ultimately, timely replacement of worn-out packing is the most effective solution for persistent leakage.
Comparison of Graphite Gland Packing with Other Sealing Materials
Understanding how graphite packing compares to other common sealing solutions can aid in material selection.
-
Vs. Carbon Fiber Gland Packing: Carbon fiber packing generally offers good high-temperature resistance and wear resistance. However, graphite packing typically boasts higher continuous temperature ratings and better self-lubricating properties, which can translate to lower friction and less wear on equipment. While carbon fiber might be more cost-effective in some scenarios, graphite often provides superior performance in extreme conditions.
-
Vs. PTFE Gland Packing: PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) packing is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness, making it ideal for highly corrosive applications. However, PTFE has a significantly lower temperature limit compared to graphite. While PTFE excels in chemical resistance at lower temperatures, graphite is the preferred choice for high-temperature and high-pressure sealing.
Graphite gland packing stands out as a highly versatile and reliable sealing material, particularly in demanding industrial applications where high temperatures, corrosive media, and efficient sealing are critical. Its unique properties make it an indispensable component in ensuring the safe and effective operation of various equipment.

 Eng
Eng  русский
русский