Why Do Metal Gasket Ring Seals Fail in Steam Turbines, and How Can You Prevent Flange Leakage?
 2026.02.04
2026.02.04
 Industry News
Industry News
- 1 Common Failure Modes of Metal Gasket Rings in Steam service
- 2 Critical Factors in Preventing Flange Leakage
- 3 Innovative Sealing Solutions from Jiangsu Jintai
- 4 Technical Recommendations for Maintenance Engineers
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 6 Whitepaper: Nofstein™ Proprietary Alloys vs. Standard 316L Stainless Steel for Extreme Steam Environments
- 7 Industry References
In high-utility power generation, the integrity of a steam turbine relies heavily on the performance of its static sealing interfaces. A metal gasket ring is often the first line of defense against catastrophic pressure loss. However, the extreme thermal gradients and mechanical stresses of steam service frequently lead to seal degradation. Jiangsu Jintai Sealing Technology Co., Ltd., founded in 2004, has spent decades researching these failure modes. Through our high-end brand, Nofstein, we provide technologically advanced sealing solutions that meet CCS classification society standards, ensuring reliability in the most demanding power and chemical environments.
Common Failure Modes of Metal Gasket Rings in Steam service
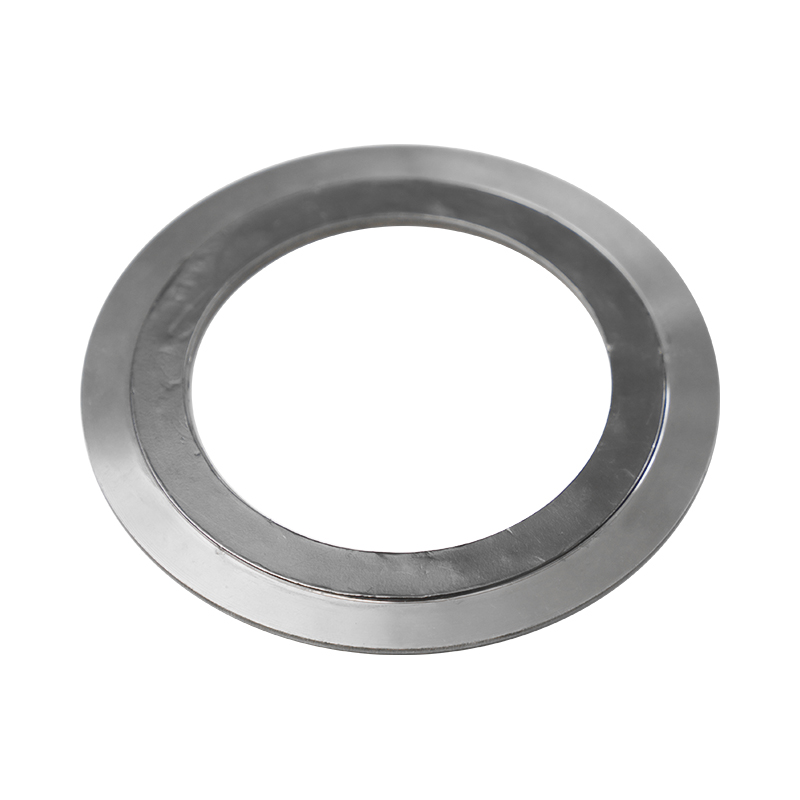
Steam turbines operate under fluctuating thermal loads that cause "flange rotation" and bolt relaxation. When a metal gasket ring fails, it is rarely due to a single factor but rather a combination of stress relaxation and surface oxidation. Unlike soft gaskets that fail through blowout, metal seals typically fail due to an inability to maintain "spring-back" or elastic recovery during thermal cycling. Engineers must distinguish between the performance of traditional solid rings and modern corrugated metal gasket for steam applications, as the latter provides better recovery under fluctuating loads.
| Failure Mechanism | Solid Metal Ring | Corrugated / Serrated Metal Gasket |
| Thermal Recovery | Poor; highly dependent on bolt preload | Excellent; geometric design aids elasticity |
| Surface Conformity | Requires high flange finish (RMS 32-63) | Better conformability to aged flange faces |
| Sealing Stress | High initial stress required | Lower seating stress required for tight seal |
Critical Factors in Preventing Flange Leakage
Preventing leakage in high-pressure steam systems requires precise adherence to high pressure RTJ gasket specifications. The Ring Type Joint (RTJ) relies on metal-to-metal interference. If the hardness of the gasket exceeds the hardness of the flange groove, the flange itself will sustain permanent damage, leading to a chronic leak path. Utilizing heat resistant metal o-ring seals can mitigate this risk in specific valve and turbine housing applications where space is constrained and high-temperature resilience is non-negotiable.
1. Material Compatibility and Hardness Ratios
A primary engineering rule is that the gasket must always be softer than the flange. In steam turbines, where temperatures can exceed 500°C, the material must also resist "stress corrosion cracking" (SCC). Choosing a stainless steel metal gasket ring with specialized heat treatment ensures the seal remains ductile enough to flow into microscopic flange irregularities without work-hardening prematurely.
2. Proper Torque and Load Distribution
- Bolt Preload: Insufficient load leads to "gapping" during start-up cycles.
- Parallelism: Misaligned flanges create uneven stress, crushing one side of the metal gasket ring while leaving the other side under-compressed.
- Surface Finish: RTJ and lens gaskets require a mirror-like finish to ensure molecular contact.
Innovative Sealing Solutions from Jiangsu Jintai
Since the production launch of our Sealing Technology Industrial Park in 2013, Jiangsu Jintai Sealing Technology Co., Ltd. has focused on bridging the gap between traditional manufacturing and high-end engineering. Our Nofstein brand adopts advanced manufacturing processes to develop industrial metal seal rings for turbines that adapt to changing market needs. By integrating specialized rubber materials and parts insulation with our metal core technology, we offer comprehensive sets for the shipping, power, and chemistry industries.
| Operational Environment | Standard Solution | Jintai/Nofstein Advanced Solution |
| High-Pressure Steam (>10MPa) | Standard Octagonal RTJ | high pressure RTJ gasket specifications compliant Nofstein Rings |
| Extreme Thermal Cycling | Flat Metal Gaskets | corrugated metal gasket for steam with Graphite Layer |
| Pneumatic/Hydraulic Control | Copper Washers | heat resistant metal o-ring seals / Specialized Rubber-Metal Parts |
Technical Recommendations for Maintenance Engineers
For B2B procurement and maintenance, it is essential to conduct regular "hot torque" procedures and utilize CCS-identified products. When selecting a replacement metal gasket ring, engineers should verify the CiT test results for environmental protection and ensure the materials meet the Chinese Academy of Coal Sciences standards for safety in hazardous zones. Our global partnerships with leading brands enable us to undertake major projects in Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa with firm confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q1: Why is gasket hardness so important for RTJ seals?
A: If the metal gasket ring is harder than the flange, it will plastically deform the flange groove instead of deforming itself. This creates permanent damage that requires expensive flange re-facing. - Q2: Can a corrugated metal gasket handle high-pressure steam?
A: Yes, a corrugated metal gasket for steam is specifically designed with ridges that create high-point contact stress, allowing it to seal at lower bolt loads while accommodating thermal expansion. - Q3: What is the benefit of "Nofstein" high-end products?
A: Nofstein products utilize advanced materials and manufacturing processes to provide higher elastic recovery and better chemical resistance than standard asbestos-free gaskets. - Q4: How does Jintai ensure the quality of its seals?
A: We maintain a sound quality management manual, CCS classification society identification, and have passed the national nonmetal and CiT environmental protection tests. - Q5: Are metal O-rings better than RTJ rings?
A: heat resistant metal o-ring seals are typically used in smaller, high-pressure enclosures or valves, whereas RTJ rings are the standard for large-diameter high-pressure piping flanges.
Whitepaper: Nofstein™ Proprietary Alloys vs. Standard 316L Stainless Steel for Extreme Steam Environments
In the power generation and petrochemical sectors, the selection of a metal gasket ring is often defaulted to 316L Stainless Steel. However, as modern steam turbines push the boundaries of supercritical and ultra-supercritical temperatures, standard alloys frequently reach their metallurgical limits. Jiangsu Jintai Sealing Technology Co., Ltd. has developed the Nofstein™ series to address the specific failure modes of stress-relaxation and intergranular corrosion found in conventional high pressure RTJ gasket specifications.
1. Metallurgical Stability and Creep Resistance
Standard 316L stainless steel undergoes significant "creep" (permanent deformation under constant stress) when exposed to temperatures exceeding 425°C. Nofstein™ alloys are engineered with controlled trace elements that stabilize the austenitic matrix, ensuring that the heat resistant metal o-ring seals maintain their elastic recovery even after prolonged exposure to 550°C+ steam.
| Technical Property | Standard 316L Stainless Steel | Nofstein™ High-Temp Alloy |
| Max Continuous Temp | 425°C (Threshold for creep) | 650°C (Stable matrix) |
| Elastic Recovery (%) | Declines rapidly after 10 cycles | Maintained > 92% after 50 cycles |
| Yield Strength at 500°C | Approx. 110 MPa | ≥ 185 MPa |
| Hardness Control | Variable (Work-hardening risk) | Precise Solution Annealed (Max 130 HB) |
2. Resistance to Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC)
Steam systems, particularly in shipping and coastal power plants, are susceptible to chloride-induced SCC. While 316L is generally resistant, the localized stress points on a metal gasket ring can trigger micro-fissures. Our industrial metal seal rings for turbines utilize an increased Nickel and Molybdenum content, which provides a significantly higher Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN), ensuring the seal remains intact in saline-rich coastal environments.
3. Geometry Optimization: The Corrugated Advantage
Beyond material science, the mechanical design of the corrugated metal gasket for steam plays a vital role. Standard solid rings require immense bolt loads to achieve "flow." Nofstein™ designs utilize a proprietary corrugation pitch that creates high-concentration sealing zones. This ensures that even if the steam turbine experiences thermal "bowing" or flange rotation, the gasket maintains contact pressure.
- Reduced Bolt Stress: Nofstein™ alloys allow for effective sealing at 30% lower torque than solid 316L rings.
- CCS & National Testing Compliance: Our alloys have passed the National Nonmetal Test and the Chinese Academy of Coal Sciences safety evaluation.
- Environmental Synergy: All Nofstein™ metal seals are 100% asbestos-free and comply with the CiT environmental protection standards.
4. Conclusion for B2B Procurement
For major projects in Eastern Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa, the TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) favors Nofstein™ alloys. Although the initial investment in a high pressure RTJ gasket specifications compliant Nofstein™ ring may be higher than 316L, the reduction in unscheduled downtime and flange repair costs provides a superior return on investment.
Jiangsu Jintai Sealing Technology Co., Ltd. continues to innovate, bridging the gap between scientific experiment and industrial manufacture to lead the world in high-end sealing technology.
Industry References
- ASME B16.20: Metallic Gaskets for Pipe Flanges - Ring-Joint, Spiral-Wound, and Jacketed.
- ISO 9001:2015: Quality management systems requirements for sealing manufacturers.
- Fluid Sealing Association (FSA): Technical Handbook on Static Seals and Gasket Failure Analysis.
- Chinese Classification Society (CCS): Quality system identification for marine and industrial sealing components.

 Eng
Eng  русский
русский









